Tender and Procurement Management | Complete Guide
What is Tender Management?
Table of Contents
Tender management is a crucial process for organizations that engage in business-to-business (B2B) transactions and procurement. It involves the systematic and strategic management of the tendering process, from identifying opportunities to submitting bids and negotiating contracts. Effective tender management can significantly impact an organization’s success by ensuring competitive bidding, maximizing value for money, and establishing long-term business relationships. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of tender management, exploring its key components, benefits, and best practices.
Understanding Tender Management
Definition of Tender
Before delving into tender management, it is essential to define what a tender is. In business, a tender is an invitation to potential suppliers or service providers to submit their proposals or bids for a particular project or contract. Tenders are commonly used by public sector organizations, government agencies, and large corporations to ensure transparency and fair competition when procuring goods and services.
The Role of Tender Management
Tender management encompasses the end-to-end process of handling tenders. It involves various stages, including identifying potential opportunities, assessing requirements, preparing bid documents, evaluating proposals, negotiating contracts, and post-contract evaluation. The primary objective of tender management is to secure contracts that align with an organization’s strategic objectives while ensuring the best possible value for money.
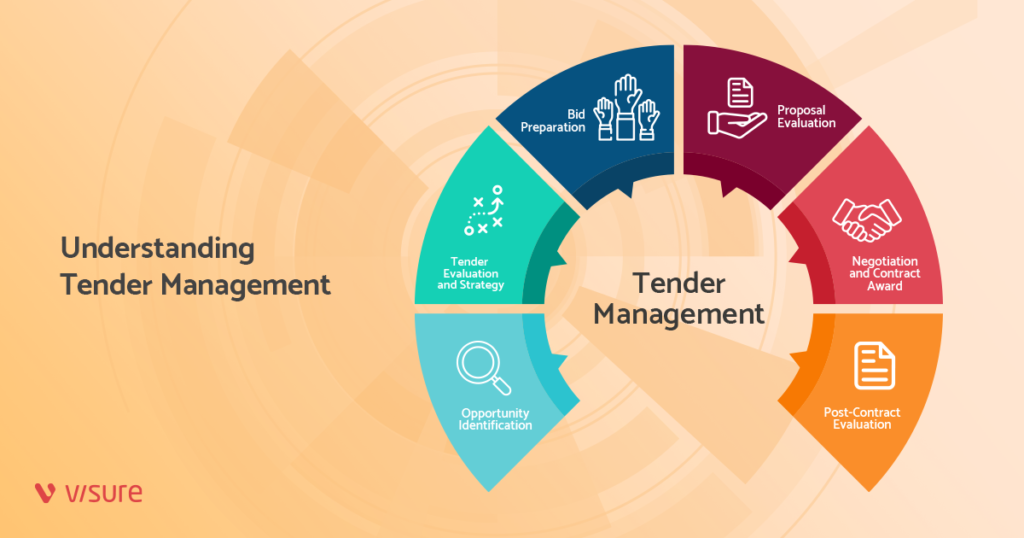
Key Components of Tender Management
To effectively manage tenders, organizations need to focus on several key components throughout the process. Let’s explore each of these components in detail:
Opportunity Identification
The first step in tender management is to identify relevant opportunities that align with an organization’s business objectives. This involves monitoring tender portals, industry publications, and networking with potential clients. By actively seeking out opportunities, organizations can ensure they stay ahead of the competition and increase their chances of securing valuable contracts.
Tender Evaluation and Strategy
Once an opportunity is identified, the next step is to evaluate the tender and develop a winning strategy. This involves carefully analyzing the requirements, assessing the scope, considering the organization’s capabilities and resources, and determining whether to pursue the opportunity. Creating a clear and well-defined strategy sets the foundation for a successful tender submission.
Bid Preparation
Bid preparation is a critical component of tender management. It involves developing a comprehensive proposal that showcases the organization’s capabilities, experience, and value proposition. The bid document should be well-structured, and persuasive, and address all the requirements outlined in the tender. Additionally, organizations must ensure that the bid is submitted within the specified deadline and in the required format.
Proposal Evaluation
After the bid submission, the tendering authority evaluates the proposals received from different bidders. The evaluation process typically involves assessing the technical, commercial, and financial aspects of each proposal. It is crucial for organizations to understand the evaluation criteria and tailor their proposals accordingly to maximize their chances of success.
Negotiation and Contract Award
If a proposal is shortlisted, the next stage involves negotiation and contract award. This phase requires effective communication and negotiation skills to finalize the terms and conditions of the contract. Organizations must strike a balance between securing favorable terms and maintaining a mutually beneficial relationship with the client. Once the negotiations are successfully concluded, the contract is awarded to the selected bidder.
Post-Contract Evaluation
Tender management does not end with a contract award. Post-contract evaluation is a crucial component that allows organizations to assess the performance of the contract and identify areas for improvement. It involves monitoring key performance indicators, tracking deliverables, and addressing any issues or disputes that may arise during the contract duration. By conducting a thorough post-contract evaluation, organizations can refine their tender management processes and enhance future performance.
Benefits of Effective Tender Management
Implementing effective tender management practices offers several benefits for organizations:
Increased Competitiveness
Proper tender management enables organizations to develop compelling bids that stand out from the competition. By thoroughly analyzing the requirements, tailoring the proposal, and highlighting unique value propositions, organizations can enhance their competitiveness and increase the likelihood of winning contracts.
Maximizing Value for Money
Through effective tender management, organizations can identify opportunities to optimize costs, negotiate favorable terms, and select suppliers or service providers that offer the best value for money. This ensures that the organization’s resources are utilized efficiently, leading to cost savings and improved profitability.
Building Strategic Partnerships
Successful tender management facilitates the establishment of long-term strategic partnerships with clients and suppliers. By delivering high-quality services or products, meeting contractual obligations, and fostering good relationships, organizations can enhance their reputation and increase the likelihood of future business opportunities.
Continuous Improvement
Engaging in tender management provides organizations with valuable insights and feedback that can be used to improve their processes, strategies, and overall performance. By conducting post-contract evaluations and incorporating lessons learned into future tender submissions, organizations can continuously enhance their tender management practices and increase their chances of success.
Tender Management Challenges
Tender management is a complex process that involves several challenges for organizations. These challenges can arise at different stages of the tendering process and require careful attention and mitigation strategies. Here are some common challenges faced in tender management:
- Intense Competition: Tender processes often attract a large number of participants, leading to intense competition among bidders. This makes it challenging for organizations to differentiate themselves and stand out from the competition. It requires thorough research, strong value propositions, and innovative approaches to increase the chances of winning the tender.
- Stringent Requirements: Tender documents often have stringent requirements and criteria that organizations must meet to qualify for consideration. These requirements may include technical specifications, financial capabilities, experience, certifications, and compliance with regulations. Meeting all the requirements while ensuring accuracy and completeness can be demanding and time-consuming.
- Limited Timeframes: Tenders typically have strict deadlines for submission, leaving organizations with limited time to prepare and submit their bids. The short timeframes can put significant pressure on teams to gather necessary information, develop comprehensive proposals, and complete all required documentation within the given timeline.
- Complex Documentation: Tender documentation can be extensive and complex, consisting of various forms, legal clauses, technical specifications, and evaluation criteria. Understanding and interpreting the documentation accurately is crucial to ensure that bids address all the requirements appropriately. The complexity of the documentation can pose challenges in terms of comprehension, alignment, and compliance.
- Lack of Information: In some cases, tender documentation may lack specific information or clarity, making it difficult for organizations to fully understand the scope and requirements of the tender. The lack of information can create uncertainties and increase the risk of misinterpretation, resulting in bids that may not precisely meet the tendering authority’s expectations.
- Resource Allocation: Tender management requires substantial resources in terms of time, personnel, and financial investment. Organizations need to allocate resources effectively to carry out thorough research, develop competitive proposals, and manage the entire tendering process. Limited resources or inadequate allocation can hinder the organization’s ability to deliver a high-quality bid.
- Coordination and Collaboration: Tender management involves coordination and collaboration among various internal teams and stakeholders. These may include sales, legal, finance, technical experts, and senior management. Ensuring effective communication, alignment, and collaboration among these stakeholders can be challenging, especially when they have different priorities and objectives.
- Risk Management: Tender management involves inherent risks, including the risk of non-compliance, legal challenges, or unforeseen circumstances. Organizations must identify and manage these risks effectively throughout the tendering process. Failing to address potential risks adequately can impact the success of the bid and the organization’s reputation.
- Changing Requirements: Tender requirements can change during the tendering process, requiring organizations to adapt their bids accordingly. These changes may include modifications to technical specifications, evaluation criteria, or terms and conditions. Keeping track of these changes and ensuring timely adjustments to the bid can be demanding, especially when multiple revisions are involved.
- Post-Bid Evaluation and Follow-up: Even after submitting the bid, organizations may face challenges during the post-bid evaluation phase. This may include addressing clarifications or negotiations with the tendering authority, competing against other shortlisted bidders, and providing additional information or documentation as requested. Effective follow-up and communication are crucial to maximize the chances of winning the contract.
To overcome these challenges, organizations need to establish robust tender management processes, allocate resources strategically, foster effective collaboration among stakeholders, invest in research and preparation, and continuously improve their bidding strategies based on past experiences. Embracing technology solutions, such as tender management software, can also streamline the process, enhance efficiency, and improve the overall success rate in tender management.
Bid vs. Tender vs. Proposal Management
In the realm of business-to-business (B2B) transactions and procurement, bid management, tender management, and proposal management are distinct processes that organizations employ to secure contracts and projects. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent different stages within the larger procurement process. In this article, we will explore the differences between bid management, tender management, and proposal management, shedding light on their unique characteristics and how they contribute to successful business development.
Bid Management
Bid management refers to the process of handling and coordinating the preparation and submission of bids in response to specific requests for proposals (RFPs) or invitations to tender. It focuses on the tactical aspects of creating and submitting a competitive bid. The key objective of bid management is to maximize the organization’s chances of winning a contract or project by presenting a compelling and tailored proposal.
Bid management involves several key activities, including:
- Bid Identification: Identifying relevant bid opportunities by monitoring bid portals, industry publications, and networking with potential clients.
- Bid Evaluation: Assessing the bid requirements, scope, and feasibility to determine whether it aligns with the organization’s capabilities and strategic objectives.
- Bid Preparation: Develop a comprehensive bid document that addresses the requirements outlined in the RFP. This includes defining the scope of work, pricing, delivery timelines, and any other relevant details.
- Coordination: Coordinating various internal departments and stakeholders involved in the bid preparation process, such as sales, finance, legal, and technical teams.
- Submission: Ensuring the bid is submitted within the specified deadline and in the required format, including any necessary documentation, samples, or certifications.
- Follow-up: Tracking the bid progress, engaging in clarifications or negotiations with the client, and addressing any queries or concerns that may arise during the evaluation phase.
Effective bid management requires close collaboration between different departments, attention to detail, and a deep understanding of the client’s requirements and evaluation criteria. It focuses on positioning the organization as the preferred bidder by highlighting its strengths, unique selling points, and value proposition.
Tender Management
Tender management encompasses the broader process of handling tenders, which are formal invitations for suppliers or service providers to submit their proposals or bids for a specific contract or project. It involves managing the end-to-end tendering process, from identifying opportunities to contract award and post-contract evaluation.
Tender management comprises various stages and activities, including:
- Opportunity Identification: Actively seeking out tender opportunities through tender portals, industry networks, and market intelligence.
- Tender Evaluation and Strategy: Assessing the tender requirements, evaluating the feasibility and fit with the organization’s capabilities, and developing a winning strategy.
- Bid Preparation: Creating a comprehensive bid document that addresses the tender requirements, showcases the organization’s capabilities and experience, and differentiates it from competitors.
- Proposal Evaluation: Participating in the evaluation process conducted by the tendering authority, which includes assessing technical, commercial, and financial aspects of the proposals received.
- Negotiation and Contract Award: Engaging in negotiations with the client to finalize the terms and conditions of the contract and ultimately securing the contract if successful.
- Post-Contract Evaluation: Conduct post-contract evaluation to monitor the performance of the contract, track deliverables, and address any issues or disputes that may arise.
Tender management aims to secure contracts that align with the organization’s strategic objectives while maximizing value for money. It requires a comprehensive understanding of the tendering process, effective communication and negotiation skills, and the ability to deliver high-quality proposals.
Proposal Management
Proposal management focuses on the strategic development and preparation of persuasive and tailored proposals in response to specific client requirements. It is a proactive approach to winning business by understanding the client’s needs and crafting a compelling solution.
Key activities involved in proposal management include:
- Client Needs Assessment: Conduct a thorough analysis of the client’s needs, challenges, and objectives to develop a deep understanding of their requirements.
- Solution Development: Creating a customized solution that addresses the client’s specific needs, showcases the organization’s expertise, and adds value to the client’s business.
- Proposal Writing: Developing a well-structured, persuasive, and compelling proposal that clearly communicates the organization’s capabilities, methodology, and value proposition.
- Graphics and Visuals: Incorporating visual elements, such as infographics, diagrams, and charts, to enhance the proposal’s visual appeal and convey information effectively.
- Quality Assurance: Conduct a thorough review and editing process to ensure the proposal is error-free, coherent, and aligned with the client’s requirements.
- Presentation: Delivering the proposal in a professional and engaging manner, whether through a formal presentation or virtual communication channels.
Proposal management emphasizes the strategic aspect of business development, focusing on understanding the client’s needs and crafting a solution that resonates with them. It requires effective communication skills, creativity, and the ability to clearly articulate the organization’s value proposition.
Tender Management Software
A tender management system (TMS) is a software solution designed to streamline and automate the tender management process. It provides organizations with a centralized platform to manage and track all aspects of the tendering process, from identifying opportunities to contract awards and post-contract evaluations.
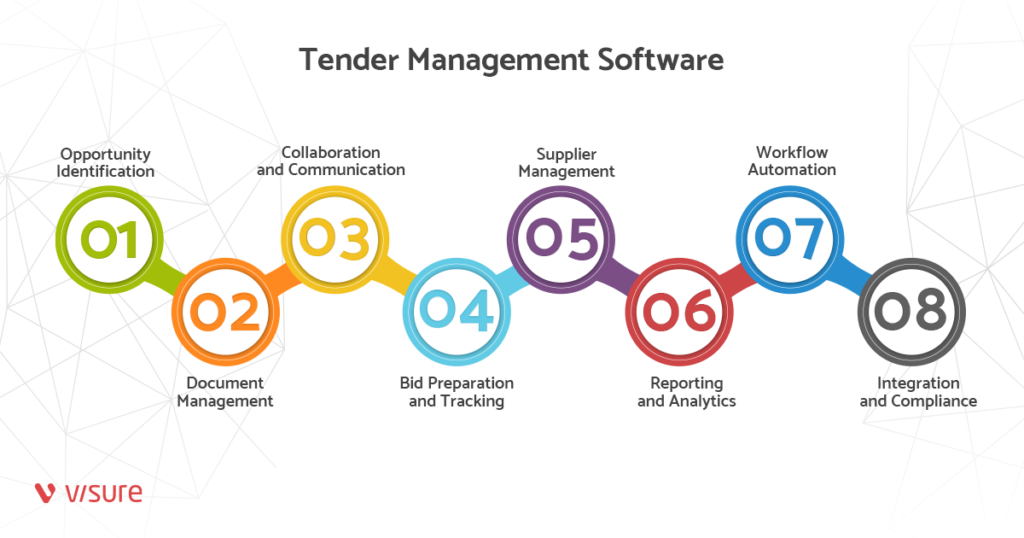
A tender management system typically offers a range of features and functionalities to facilitate efficient tender management, including:
- Opportunity Identification: The TMS allows organizations to search and identify relevant tender opportunities by integrating with tender portals, databases, and market intelligence sources. It provides notifications and alerts for new opportunities that match predefined criteria.
- Document Management: The TMS enables organizations to store, organize, and manage all tender-related documents in a secure and centralized repository. This includes RFP documents, bid templates, supporting documents, and historical tender data.
- Collaboration and Communication: The TMS facilitates collaboration among different departments and stakeholders involved in the tendering process. It allows team members to collaborate on bid preparation, share documents, and communicate internally within the system.
- Bid Preparation and Tracking: The TMS provides tools to create, edit, and manage bid documents within the system. It allows organizations to track the progress of bid preparation, assign tasks to team members, and set deadlines to ensure timely submission.
- Supplier Management: The TMS helps organizations manage their supplier database, including maintaining supplier profiles, tracking performance, and evaluating past engagement. This enables efficient supplier selection and engagement during the tendering process.
- Reporting and Analytics: The TMS generates reports and analytics to provide insights into the organization’s tendering activities. It offers visibility into bid success rates, bid performance, key metrics, and trends, helping organizations make data-driven decisions and improve their tendering strategies.
- Workflow Automation: The TMS automates routine tasks and workflows, such as document generation, approval processes, and notification reminders. This helps streamline the tender management process, reduce manual errors, and improve efficiency.
- Integration and Compliance: The TMS integrates with other business systems, such as customer relationship management (CRM) or enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, to ensure seamless data exchange and workflow integration. It also helps organizations ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and internal policies.
Implementing a tender management system offers several benefits to organizations, including improved efficiency, enhanced collaboration, increased visibility, reduced administrative burden, and better control over the tendering process. It allows organizations to streamline their tender management activities, save time and resources, and increase their chances of winning contracts through more effective and strategic bidding.
Visure Requirements ALM Platform
Document Management: Producing High-Quality RFI/RFPs
The Visure Requirements ALM Platform offers robust document management capabilities that are crucial for producing high-quality Requests for Information (RFIs) and Requests for Proposals (RFPs) during the tender management process. The platform provides a centralized repository where organizations can store, manage, and version-control all tender-related documents.
With Visure’s document management functionality, organizations can easily collaborate on creating and editing RFIs and RFPs. Multiple stakeholders can contribute to the document simultaneously, ensuring efficient collaboration and reducing the risk of version conflicts. The platform allows for real-time commenting and annotation, facilitating effective communication and feedback among team members.
Additionally, Visure’s document management features enable organizations to maintain a library of reusable content and templates. This helps standardize the tendering process and ensures consistency across multiple RFIs and RFPs. By leveraging pre-defined templates and reusable content, organizations can save time, improve accuracy, and produce high-quality documents that effectively communicate their requirements and expectations to potential suppliers.
Traceability
Effective traceability is crucial in tender management, as it enables organizations to establish clear connections between various tender artifacts, such as requirements, specifications, and bids. The Visure Requirements ALM Platform provides comprehensive traceability features that allow organizations to track and manage the relationships between different tender-related items.
With Visure’s traceability capabilities, organizations can easily trace bid elements back to the specific tender requirements they address. This ensures that all bid elements are aligned with the client’s needs and enables organizations to demonstrate compliance with the tender specifications.
Furthermore, Visure’s bid traceability features enable organizations to trace the impact of changes made during the bid preparation process. This helps ensure that any modifications or updates to the bid are properly evaluated and do not inadvertently introduce conflicts or inconsistencies.
Workflows
Visure Requirements ALM Platform offers powerful workflow management capabilities that streamline the tender management process. Workflows in Visure allow organizations to define and automate the sequential and parallel activities involved in tender management, ensuring consistent and efficient execution of tasks.
By configuring workflows within the platform, organizations can establish predefined steps, assign responsibilities to team members, and set up approval processes for various tender-related activities. This includes activities such as bid preparation, document review and approval, stakeholder feedback, and submission tracking.
Visure’s workflow automation minimizes manual effort, reduces the risk of errors, and provides visibility into the status of different tender management activities. This helps organizations stay on track, meet deadlines, and ensure that all necessary steps are completed before bid submission.
Quality Analyzer
The Visure Requirements ALM Platform includes a powerful Quality Analyzer that supports the evaluation and analysis of tender-related artifacts. The Quality Analyzer allows organizations to define quality rules, guidelines, and best practices specific to the tender management process.
By leveraging the Quality Analyzer, organizations can assess the quality of their tender artifacts, such as RFIs, RFPs, and bid documents, against predefined criteria. This ensures that the submitted documents meet the required quality standards, increasing the likelihood of successful bid evaluation and selection.
The Quality Analyzer also provides automated checks for consistency, completeness, and compliance with regulatory and contractual requirements. This helps organizations identify and rectify any gaps or deficiencies in the tender artifacts before submission, ensuring a high-quality bid that stands out among competitors.
Attributes
Visure Requirements ALM Platform allows organizations to define and manage attributes for tender-related artifacts. Attributes provide additional metadata and context to tender artifacts, facilitating effective organization, filtering, and searching.
By defining custom attributes specific to the tender management process, organizations can capture and track additional information relevant to their bids. This may include information such as bid status, target market, pricing details, or contractual terms. The ability to define custom attributes ensures flexibility and adaptability to different tender requirements and organizational needs.
Attributes in Visure also enable organizations to generate reports and analytics based on specific criteria. This supports data-driven decision-making, provides insights into the tendering process, and helps organizations identify trends and areas for improvement.
Data Models
Visure Requirements ALM Platform offers flexible data modeling capabilities that allow organizations to define custom data models for tender management. Data models help organizations structure and organize tender-related information according to their specific requirements.
With Visure’s data modeling capabilities, organizations can define entities, relationships, and attributes that accurately represent the various components of the tender management process. This includes entities such as RFIs, RFPs, bids, requirements, stakeholders, and evaluation criteria.
By creating custom data models, organizations can capture and manage tender-specific information effectively. This ensures that all relevant data is properly structured and accessible, facilitating efficient tender management and decision-making.
Stakeholder Collaboration
Effective collaboration among stakeholders is crucial in tender management, and the Visure Requirements ALM Platform provides robust features to facilitate stakeholder collaboration throughout the tendering process.
Visure enables stakeholders to collaborate on tender-related activities by providing a centralized platform where they can share information, exchange feedback, and contribute to the tender preparation. Stakeholders can securely access the platform, view and comment on tender artifacts, and engage in discussions within the context of the documents.
This collaboration functionality enhances communication, fosters transparency, and ensures that all stakeholders have visibility into the progress and status of tender-related activities. It helps streamline decision-making, gather valuable input from subject matter experts, and ensure that all perspectives are considered in the bid preparation process.
Conclusion
To sum up, effective tender management can provide many benefits from greatly reducing the costs of preparation to a stronger return on investments. From understanding what tender management is and its role in successful projects to knowing the top components and potential challenges, consider these topics when beginning your own project. Tender management processes can be simplified with various software options such as Visure Requirements ALM Platform.
Take some time to understand your project objectives and determine how implementing effective tender management practices could help reach these goals. Don’t forget that it often helps to consult with experts who will have insight on how to best utilize this process. Try out the free 30-day trial at Visure Requirements ALM Platform and, not only will you be one step closer to accomplishing your business objectives but, you may even save time and effort later down the line. When handled properly, tender management initiatives can result in end financial rewards so take advantage of every opportunity for success!
Don’t forget to share this post!
Start Gaining End-to-End Traceability Across Your Projects with Visure Today
Start 30-day Free Trial Today!


