Test Management | Complete Guide
Medical Devices Test Management Tools & Process
Table of Contents
Medical devices play a crucial role in modern healthcare, providing diagnostic, therapeutic, and monitoring capabilities that save lives and improve patient outcomes. Ensuring the safety and effectiveness of these devices is paramount, and one essential aspect of this process is rigorous testing. Medical device test management tools and processes are vital components in the development and maintenance of these devices, helping manufacturers meet regulatory requirements, minimize risks, and deliver high-quality products. In this article, we’ll explore the world of medical device testing, including the tools and processes that support it.
What is Medical Devices Test Management?
Test management in the medical device industry is the process of overseeing and controlling all aspects of testing activities to ensure that medical devices meet the necessary regulatory, safety, and quality standards. It involves the strategic planning, coordination, and monitoring of testing processes to verify that medical devices are safe, effective, and reliable for their intended use. Test management in this industry is essential to minimize risks, comply with regulatory requirements, and maintain product quality. It encompasses the organization and administration of all testing efforts, with a focus on achieving thorough and documented testing to meet regulatory and safety standards.
The Importance of Medical Device Test Management
Testing is an integral part of the medical device development lifecycle. It ensures that devices are safe, reliable, and effective for their intended use, reducing the risk of harm to patients and healthcare providers. The consequences of inadequate testing can be severe, potentially leading to product recalls, legal liabilities, and, most importantly, patient harm. Therefore, comprehensive and well-structured testing processes are essential in the medical device industry.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory bodies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), have stringent requirements for medical device testing. Manufacturers must demonstrate that their products meet these regulatory standards before they can be marketed. Compliance with regulations, such as the FDA’s 510(k) or PMA processes, requires robust testing documentation and data.
Risk Mitigation
Testing allows manufacturers to identify and mitigate potential risks associated with medical devices. It helps identify design flaws, usability issues, and any other factors that may pose a threat to patients or users. By addressing these issues during the development process, manufacturers can reduce the likelihood of adverse events and costly post-market modifications.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is a cornerstone of medical device manufacturing. Robust testing processes are essential for maintaining product quality. These processes help identify defects and inconsistencies in manufacturing, ensuring that devices meet the desired specifications and performance standards.
The Medical Device Test Management Process
The medical device testing process is a multi-faceted approach that includes various stages. These stages are executed to verify that a medical device complies with design specifications, regulatory requirements, and user expectations. Here are the key stages of the medical device testing process:
1. Test Planning
Test planning is the foundation of the testing process. In this stage, a comprehensive test plan is developed, outlining the testing objectives, scope, methods, and acceptance criteria. The test plan ensures that all testing activities are aligned with the device’s intended use and regulatory requirements. It also identifies the resources and tools needed for testing.
2. Test Design
Test design involves creating detailed test cases and test protocols based on the test plan. Test cases define the steps to be followed during testing, including the test environment, test data, and expected outcomes. The objective is to design tests that thoroughly assess the device’s performance, safety, and effectiveness.
3. Test Execution
Test execution is the phase where the actual testing takes place. Testers carry out the defined test cases, record results, and document any deviations or issues encountered during testing. This stage ensures that the device functions as expected and complies with regulatory requirements.
4. Test Reporting
After the completion of testing, a test report is generated. This report summarizes the test results, including pass/fail criteria, deviations, and any issues identified. Test reports are crucial for demonstrating compliance with regulatory requirements and for transparency in product development.
5. Test Documentation
Comprehensive documentation of the testing process is essential. This includes test plans, test cases, test protocols, test reports, and any associated records. Proper documentation is critical for regulatory submissions and audits.
6. Risk Analysis
In parallel with testing, a risk analysis is conducted to identify and assess potential risks associated with the medical device. Risk analysis helps manufacturers prioritize and address the most critical issues during the development process.
7. Usability Testing
Usability testing evaluates the device’s user interface, including its ease of use, user feedback, and ergonomic design. Usability is a critical factor in the development of medical devices, as difficult-to-use devices can lead to errors and adverse events.
8. Validation and Verification
Validation ensures that the device meets its intended use and user needs, while verification confirms that the device meets its design and performance specifications. Both processes are essential to demonstrate that the device is safe and effective.
9. Regulatory Submissions
Once testing is complete, the data and documentation are compiled for submission to regulatory authorities. This step is necessary to obtain the necessary approvals for marketing and selling the medical device.
International Standards for Medical Device Test Management
Yes, medical device test management must comply with various standards and regulations to ensure the safety, effectiveness, and quality of medical devices. Some of the key standards and regulatory frameworks that govern medical device testing include:
- ISO 13485:
- ISO 13485 is an international standard for quality management systems specific to the medical device industry. It outlines requirements for the design, development, production, and post-market surveillance of medical devices. Compliance with ISO 13485 is often a prerequisite for regulatory approvals.
- ISO 13485:
- FDA Regulations:
- In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) governs medical device testing through various regulations, including 21 CFR Part 820 (Quality System Regulation) and 21 CFR Part 11 (Electronic Records; Electronic Signatures). These regulations set requirements for quality systems and electronic records management.
- FDA Regulations:
- EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In-vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR):
- The European Union has introduced the MDR and IVDR, which set stringent requirements for medical device testing, including clinical evaluations, risk assessments, and post-market surveillance. Compliance with these regulations is essential for devices marketed in the EU.
- EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In-vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR):
- IEC 60601:
- IEC 60601 is a series of international standards that pertain to the safety and performance of medical electrical equipment. It covers aspects such as electrical safety, electromagnetic compatibility, and essential performance.
- IEC 60601:
- ISO 14971:
- ISO 14971 is an international standard for risk management in medical devices. It provides guidelines for identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with medical devices throughout their lifecycle.
- ISO 14971:
Medical device manufacturers are expected to adhere to these standards and regulations to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of their products. Compliance with these standards is often a prerequisite for regulatory approvals and market access. Moreover, effective test management is critical in ensuring that the testing processes align with these standards and requirements, allowing for the successful development and commercialization of medical devices.
Essential Toolkit for Medical Devices Test Management
Testing is a crucial aspect of ensuring the safety, effectiveness, and quality of medical devices. Different types of tests are performed on medical devices to verify their performance and safety. Additionally, various tools and techniques are used to conduct these tests effectively and efficiently. Here, we will explore the common types of tests and the tools and techniques used in the medical device industry.
Common Types of Tests for Medical Devices
- Functional Testing:
- Aim: To verify that the medical device performs its intended functions correctly and consistently under normal and abnormal conditions.
- Testing Includes: Verification of user interface, input/output functionality, data processing accuracy, alarm systems, sensor reliability, and battery life under different scenarios.
- Functional Testing:
- Performance Testing:
- Aim: To evaluate the medical device’s ability to meet its technical specifications and requirements, including accuracy, precision, sensitivity, specificity, reliability, and durability.
- Testing Involves: Assessment of physical, chemical, biological, electrical, mechanical, or environmental properties of the device to ensure it meets defined performance standards.
- Performance Testing:
- Usability Testing:
- Aim: To assess how easy and intuitive it is for intended users to operate and interact with the medical device.
- Testing Covers: User satisfaction, preferences, errors, feedback, training requirements, and overall user experience.
- Usability Testing:
- Compatibility Testing:
- Aim: To check whether the medical device can work seamlessly with other devices or systems it is intended to be used with or connected to.
- Testing Encompasses: Verification of interoperability, integration capabilities, communication protocols, and data exchange functionalities.
- Compatibility Testing:
- Safety Testing:
- Aim: To ensure that the medical device does not pose any harm or risk to users, patients, or the environment.
- Testing Includes: Examination of biocompatibility, sterility, toxicity, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), electrical safety, radiation safety, and other safety aspects.
- Safety Testing:
Tools and Techniques for Medical Device Testing
- Test Automation Tools:
- Purpose: To automate various aspects of test execution, improving efficiency, consistency, and test coverage.
- Benefits: Reduces human errors, saves time and resources, increases test coverage and consistency, and enhances test quality and reliability.
- Examples: Selenium, TestComplete, and other automation frameworks help streamline the testing process for medical devices.
- Test Automation Tools:
- Test Management Tools:
- Purpose: To manage and organize the entire test process, including planning, design, execution, monitoring, reporting, and documentation.
- Benefits: Facilitates coordination and communication among test team members and stakeholders, tracks and controls test progress and status, measures and improves test performance and efficiency, and ensures test traceability and compliance.
- Examples: Quality Center, Jira, and other test management tools assist in managing complex testing workflows.
- Test Management Tools:
- Test Equipment:
- Purpose: To provide inputs or outputs to the medical device under test, measure its properties or behavior, and simulate real-world conditions.
- Benefits: Supports real-world scenario simulation, generates or captures data or signals, and verifies or validates test results.
- Examples: Instruments such as oscilloscopes, multimeters, signal generators, thermocouples, and specialized medical testing equipment are used to facilitate the testing process.
- Test Equipment:
By employing these common types of tests and utilizing appropriate tools and techniques, the medical device industry can ensure the development and maintenance of high-quality, safe, and effective devices that meet regulatory requirements and benefit patients and healthcare providers.
Medical Device Test Management Tools
To streamline and optimize the testing process for medical devices, various test management tools are available. These tools assist in test planning, design, execution, and reporting. They help ensure that testing is efficient, well-documented, and compliant with regulatory requirements. Some popular medical device test management tools include:
Visure Solutions:
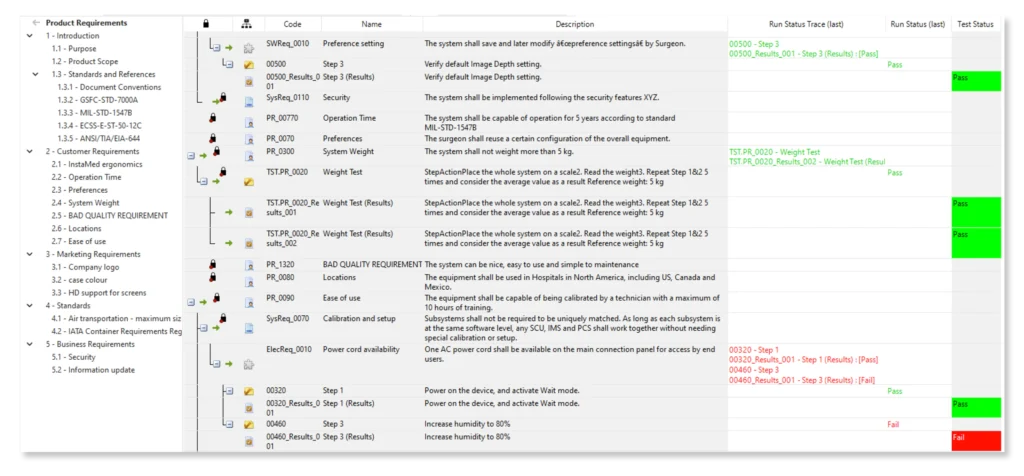
Visure Solutions provides a comprehensive requirements and test management tool specifically designed for highly regulated industries like the medical device sector. Their platform enables efficient test planning, execution, and traceability to ensure compliance with regulatory standards and documentation requirements. Visure Solutions is known for its flexibility and adaptability, making it an excellent choice for streamlining testing processes in the medical device industry.
TestRail:
TestRail is a widely used test management tool that allows teams to plan, track, and manage testing activities. It provides features for test case management, test execution, and detailed reporting. TestRail is highly configurable and can be tailored to meet the specific needs of the medical device industry, ensuring that testing aligns with regulatory requirements.
qTest:
qTest is a comprehensive test management tool for quality assurance and testing teams. It offers test case management, test execution, and defect tracking capabilities. qTest facilitates collaboration among team members and integrates seamlessly with various testing tools, making it a powerful solution for managing medical device testing processes.
JIRA:
JIRA, developed by Atlassian, is a versatile project management and issue-tracking tool. While not exclusively a test management tool, JIRA can be configured to support test case management, test execution, and reporting. Its flexibility and customizable nature make it a popular choice for creating a complete testing solution for medical devices, particularly when integrated with other tools.
TestLodge:
TestLodge is a straightforward yet effective test management tool designed for small to medium-sized teams. It offers test case management, test execution, and reporting features. Known for its user-friendly interface and ease of use, TestLodge is suitable for teams with varying levels of technical expertise, making it an ideal choice for medical device testing.
HP ALM (Application Lifecycle Management):
HP ALM is an enterprise-level test management tool that provides extensive features for test planning, execution, defect management, and reporting. It is particularly well-suited for large organizations with complex testing processes. HP ALM integrates with other tools and is highly customizable to meet specific testing needs in the medical device industry.
PractiTest:
PractiTest is a test management and quality assurance platform that offers a comprehensive set of tools for managing the testing process. It allows for efficient test case management, test execution, and defect tracking. PractiTest also provides integration options and customizable workflows to suit the specific requirements of the medical device industry.
Each of these test management tools has its strengths and is suitable for different types and scales of medical device testing projects. Choosing the right tool depends on factors such as the specific testing needs, team size, budget, and the complexity of the medical device being developed.
Challenges in Medical Device Test Management
Testing medical devices is a complex and highly regulated process, and it comes with its set of challenges. Here, we’ll delve into the key challenges in medical device testing:
1. Regulatory Complexity:
The medical device industry is subject to a web of stringent regulations and standards enforced by various regulatory bodies worldwide. Navigating through these complex and ever-evolving requirements can be challenging. Manufacturers must ensure that their devices comply with regulations such as the FDA’s 510(k) or PMA processes in the United States, CE marking in Europe, and other country-specific requirements. Failure to meet these regulations can result in significant delays, financial losses, and legal issues.
2. Rapid Technological Advancements:
Advancements in technology are occurring at an unprecedented pace. Medical devices are becoming increasingly sophisticated, incorporating cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence, IoT connectivity, and miniaturized sensors. These advancements create challenges in testing, as ensuring the safety and effectiveness of complex, high-tech devices is more demanding and resource-intensive.
3. Interoperability:
Many medical devices need to work in conjunction with other healthcare systems and technologies, such as electronic health records (EHRs) and hospital information systems. Ensuring that a medical device seamlessly integrates and interoperates with other systems is a significant challenge. Interoperability issues can lead to data inconsistencies, communication breakdowns, and potential patient harm.
4. Data Security and Privacy:
Connected medical devices, which are becoming increasingly common, pose unique challenges related to data security and privacy. These devices collect, transmit, and store sensitive patient data. Ensuring the security of patient information and the device itself is paramount. Security vulnerabilities can lead to data breaches, compromising patient privacy and potentially causing harm.
5. Validation of Software-Intensive Devices:
Many modern medical devices rely heavily on software for their operation. Validating software is a complex task, and the risk of software bugs or vulnerabilities can be particularly high in software-intensive devices. Ensuring the reliability and safety of the software component is a challenge, as any software malfunction can have serious consequences.
6. Human Factors and Usability:
Usability issues with medical devices can lead to user errors, adverse events, and patient harm. Evaluating the device’s user interface, ergonomics, and overall usability is a challenge. It requires specialized usability testing and human factors engineering to identify and mitigate potential issues.
7. Scalability:
Scaling up testing processes to meet the demands of mass production can be challenging. As a medical device moves from the prototype stage to full-scale manufacturing, ensuring consistent quality and performance across all units is essential.
8. Resource Constraints:
Allocating the necessary resources, including skilled personnel and state-of-the-art testing equipment, can be challenging, particularly for smaller medical device companies. Testing budgets and timelines must be managed carefully to meet regulatory and quality standards.
9. Continuous Monitoring and Post-Market Surveillance:
Medical devices continue to evolve even after they enter the market. Manufacturers are responsible for post-market surveillance, including monitoring the device’s performance and responding to any reported issues or adverse events. This ongoing surveillance and management of post-market data can be a considerable challenge.
Addressing these challenges requires a combination of expertise, robust testing processes, and the use of advanced testing tools and technologies. Manufacturers must be proactive in adapting to regulatory changes, staying updated on industry best practices, and investing in the development and improvement of their testing methodologies to ensure the safety and effectiveness of medical devices.
Best Practices for Medical Device Test Management
Test management in the medical device industry is a critical component of ensuring product safety, quality, and compliance with regulatory standards. Following best practices is essential to streamline the testing process and mitigate risks effectively. Here are some key best practices for test management in the medical device industry:
- Establish a Comprehensive Test Plan:
- Develop a detailed test plan that outlines testing objectives, scope, methods, and acceptance criteria.
- Ensure alignment with the device’s intended use and regulatory requirements.
- Identify necessary resources, including personnel, equipment, and testing tools.
- Establish a Comprehensive Test Plan:
- Use Traceability:
- Implement traceability to link test cases and test results to specific requirements, design inputs, and risk analyses.
- This ensures that all testing activities are directly related to product specifications and regulatory requirements.
- Use Traceability:
- Implement Risk-Based Testing:
- Perform risk analysis and prioritize testing activities based on the identified risks.
- Focus more testing efforts on high-risk areas to mitigate potential hazards effectively.
- Implement Risk-Based Testing:
- Document Extensively:
- Maintain thorough and well-organized documentation throughout the testing process.
- Document test plans, test cases, test protocols, test results, and any deviations or issues encountered.
- Document Extensively:
- Usability Testing:
- Conduct usability testing to evaluate the device’s user interface and user experience.
- Ensure that the device is easy to use, minimizing the potential for user errors and adverse events.
- Usability Testing:
- Validation and Verification:
- Perform both validation and verification to confirm that the device meets its intended use and design specifications.
- Validation ensures the device addresses user needs, while verification confirms design compliance.
- Validation and Verification:
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Stay up-to-date with relevant regulatory requirements, such as FDA’s 510(k) or PMA processes, and ensure full compliance.
- Keep track of any changes or updates in regulations that may impact testing procedures.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Data Security and Privacy:
- Prioritize data security and privacy concerns, especially for connected medical devices.
- Implement robust measures to protect patient data and ensure device security.
- Data Security and Privacy:
- Interoperability Testing:
- If the device interacts with other healthcare systems or technologies, perform interoperability testing to ensure compatibility.
- This is crucial for the seamless operation of the device in clinical settings.
- Interoperability Testing:
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement:
- Continuously monitor and evaluate the testing process to identify areas for improvement.
- Implement feedback loops and adjust testing procedures based on lessons learned from previous testing cycles.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement:
- Cross-Functional Collaboration:
- Encourage collaboration among multidisciplinary teams, including engineers, regulatory experts, quality assurance professionals, and clinicians.
- Foster open communication to address issues and ensure that testing aligns with all stakeholders’ needs.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration:
- Training and Competency:
- Ensure that the testing team is adequately trained and possesses the necessary expertise.
- Regularly update team members on changes in regulations and best practices.
- Training and Competency:
- Test Management Tools:
- Implement test management tools like TestRail, qTest, JIRA, TestLodge, and Visure Solutions to streamline and optimize the testing process.
- These tools help in test case management, test execution, and reporting.
- Test Management Tools:
- Regulatory Submission Preparation:
- Prepare and maintain all documentation and data required for regulatory submissions.
- Ensure that the test results and documentation are readily available for audits and approvals.
- Regulatory Submission Preparation:
- Risk Mitigation and Contingency Planning:
- Identify potential issues and risks during testing and develop contingency plans to address them.
- Be proactive in addressing any obstacles that may arise during testing.
- Risk Mitigation and Contingency Planning:
By following these best practices, medical device manufacturers can navigate the complexities of the testing process effectively, ensuring that their devices meet regulatory requirements, are safe for use, and deliver high-quality outcomes for patients and healthcare providers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective test management is essential in the medical device industry to ensure the safety, quality, and regulatory compliance of these critical products. Various types of tests, such as functional, performance, usability, compatibility, and safety testing, play a pivotal role in verifying a device’s functionality and mitigating risks. The use of specialized tools and techniques, including test automation and management tools, along with the right test equipment, streamlines the testing process, improves efficiency, and ensures thorough documentation. Notably, Visure Solutions stands out as a great choice for medical device testing due to its flexibility, adaptability, and dedicated focus on highly regulated industries. To experience the benefits of Visure Solutions, we encourage you to check out the free 30-day trial at Visure and discover how it can optimize your medical device testing process.
Don’t forget to share this post!
Start Gaining End-to-End Traceability Across Your Projects with Visure Today
Start 30-day Free Trial Today!