DO-254 Certification Guide
Introduction to the DO-254 Standard Certification Compliance Guide
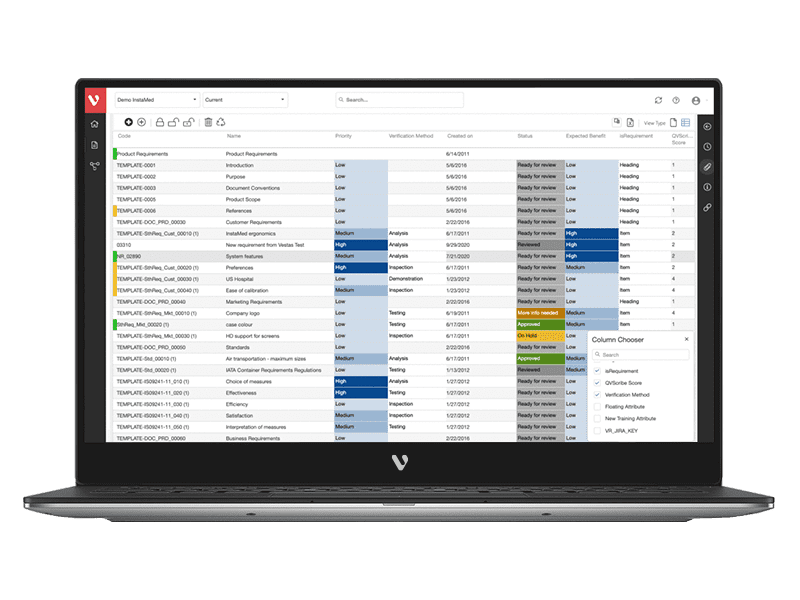
Aviation systems are becoming increasingly complex, with more and more data being generated by aircraft each day. This data can include information on engine health, fuel status, rotor blade maintenance, traffic and route statistics, cockpit information, etc. In order to handle this large volume of critical data safely and effectively, aviation authorities have put in place a number of guidelines that need to be followed.
The DO-254 standard is one such guideline, which deals with the design assurance of airborne electronic hardware. In this guide, we will take a closer look at the DO-254 standard and its implications for aircraft safety.
1. Airborne Hardware Certification Intro
A detailed overview of airborne hardware certification, including its importance, the certification process, and the regulatory requirements that must be met to obtain certification.
2. DO-254 Certification Process
An overview of the DO-254 certification process, including the steps involved in the certification process, the importance of DO-254 certification
3. DO-254 Tools & Trainings
An overview of DO-254 tools and training, including the different types of tools and trainings available, their benefits, and how they can support the DO-254 certification process.
4. Advanced DO-254 Topics
An overview of advanced DO-254 topics, including their importance, the areas they cover, and how they can support the DO-254 certification process.
5. DO-254 Resources
An overview of DO-254 resources, including the different types of resources available, their benefits, and how they can support the DO-254 certification process.
Don’t forget to share this post!
Start Gaining End-to-End Traceability Across Your Projects with Visure Today
Start 30-day Free Trial Today!