Introduction
DO-254, also known as the “Design Assurance Guidance for Airborne Electronic Hardware,” is a critical standard developed by RTCA for ensuring the safety and reliability of airborne electronic hardware used in civil aviation. It applies to complex electronic components used in avionics systems, including both custom-developed and Commercial Off-the-Shelf (COTS) hardware.
This standard mandates comprehensive planning, design, verification, and validation processes to ensure hardware functions as intended, reducing risks associated with failures during flight operations.
Relevance for Complex Electronic Hardware (CEH)
DO-254 primarily focuses on Complex Electronic Hardware (CEH), such as:
- Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs): Reconfigurable integrated circuits used for complex processing functions.
- Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs): Custom-designed chips tailored for specific functions in avionics systems.
Given the intricate designs and functionalities of CEH, adherence to DO-254 ensures they meet strict performance and safety requirements.
Importance of Compliance with RTCA DO-254 for Airborne Electronic Hardware
Compliance with RTCA DO-254 is essential for achieving airworthiness certification from aviation authorities like the FAA and EASA. Key benefits include:
- Enhanced Safety: Mitigates risks of hardware failures in critical systems.
- Regulatory Approval: Required for certification of new and modified avionics systems.
- Structured Development Process: Promotes robust design, verification, and validation methodologies.
As aviation systems become more sophisticated, ensuring compliance with DO-254 is essential for reliable and safe avionics hardware development.
What Is RTCA DO-254?
RTCA DO-254, formally titled “Design Assurance Guidance for Airborne Electronic Hardware,” was developed by RTCA, Inc. and EUROCAE in collaboration with aviation industry experts. First released in 2000, this standard provides comprehensive guidance for the design and verification of airborne electronic hardware used in civil aviation systems.
The primary goal of DO-254 is to ensure that all complex electronic hardware functions safely and reliably within avionics systems, thereby supporting the airworthiness certification process required by authorities such as the FAA and EASA.
Key Requirements and Compliance Framework
DO-254 outlines specific processes and documentation requirements to achieve compliance, including:
- Planning: Creation of key documents such as the Plan for Hardware Aspects of Certification (PHAC), Hardware Design Plan (HDP), and Hardware Verification Validation Plan (HVVP).
- Requirements Definition: Establishing detailed and testable hardware requirements for avionics systems.
- Design Implementation: Following structured design processes for developing electronic hardware.
- Verification and Validation (V&V): Comprehensive testing and verification to ensure compliance with defined requirements.
- Traceability: Maintaining traceability between requirements, design, and verification results.
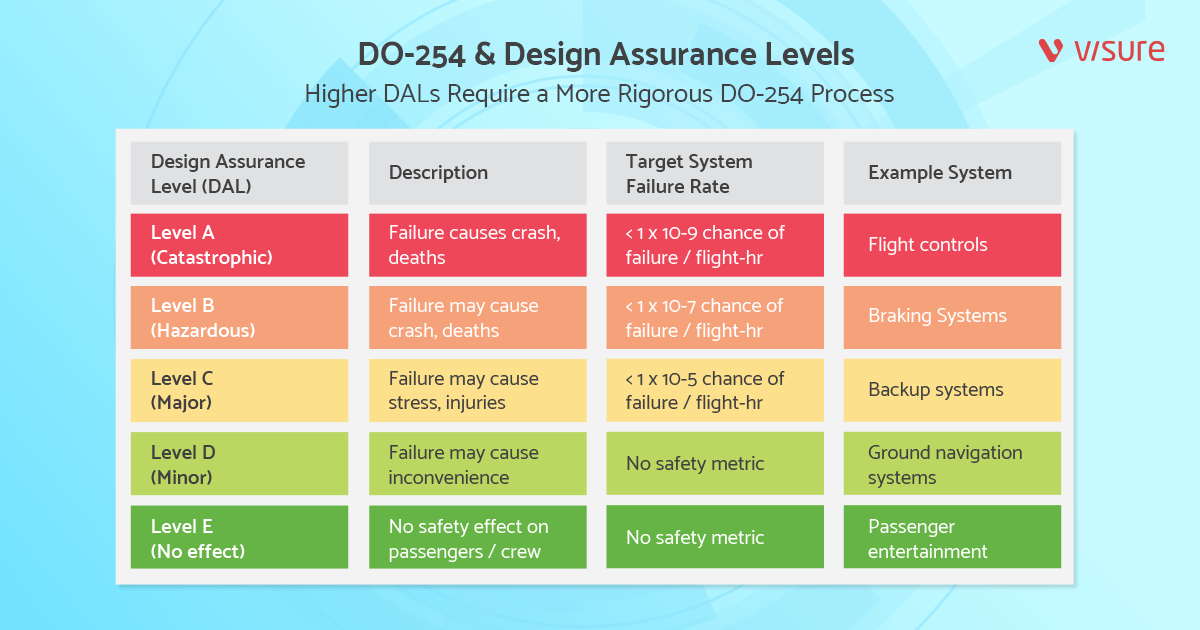
DO-254 assigns Design Assurance Levels (DAL) based on the criticality of hardware functions to flight safety, ranging from A (most critical) to E (least critical).
Importance of DO-254 for Aviation Safety
The importance of RTCA DO-254 in aviation safety cannot be overstated:
- Mitigation of Hardware Failures: Ensures robust design processes that reduce the risk of system failures during flight operations.
- Airworthiness Certification: Serves as a prerequisite for regulatory certification of new and modified avionics systems.
- Structured Development Process: Promotes a disciplined and traceable approach to hardware design and verification.
- Support for Complex Electronic Hardware (CEH): Facilitates compliance for hardware such as FPGAs and ASICs, which are widely used in modern avionics.
By adhering to DO-254, avionics manufacturers can confidently develop and certify safe and reliable hardware systems for critical airborne functions.
Key Elements of DO-254 Compliance
DO-254 Process Overview
Stages Involved in DO-254 Compliance
The DO-254 compliance process consists of several key stages:
- Planning: Defining the approach for hardware development, verification, and certification.
- Requirements Definition: Establishing clear, complete, and testable hardware requirements.
- Design Implementation: Developing hardware based on approved specifications.
- Verification and Validation (V&V): Ensuring hardware meets requirements through rigorous testing and analysis.
- Certification Support: Providing evidence to authorities such as FAA or EASA for airworthiness approval.
Essential Documentation for DO-254
Proper documentation is crucial for demonstrating compliance, including:
- Hardware Design Plan (HDP): Describes the overall approach to hardware development and verification.
- Hardware Verification and Validation Plan (HVVP): Details the V&V strategies, tools, and methods.
- Plan for Hardware Aspects of Certification (PHAC): Outlines the certification process, including compliance objectives, documentation strategy, and design assurance level assignment.
FDAL and IDAL
- Functional Design Assurance Level (FDAL): Indicates the safety criticality of hardware functions, ranging from Level A (catastrophic) to Level E (no safety effect).
- Item Design Assurance Level (IDAL): Assigns assurance levels to specific components within the system based on their role in overall functionality and safety.
DO-254 Certification Planning
Best Practices for DO-254 Compliance Planning
- Early Planning: Begin certification planning during the project’s initial phase.
- Comprehensive PHAC: Clearly define the certification strategy and roles.
- Incorporate Traceability: Ensure traceability between requirements, design, and verification activities.
- Stakeholder Collaboration: Involve key stakeholders, including certification authorities, early in the process.
Critical Elements for a Comprehensive PHAC
- Defined objectives and scope of certification
- Assignment of DAL levels for hardware components
- Development and verification processes
- Configuration management strategies
Challenges and Solutions in DO-254 Certification
- Challenge: Managing extensive documentation and traceability requirements
Solution: Leverage automated DO-254 tools for documentation management - Challenge: Achieving accurate DAL level assignments
Solution: Conduct thorough hazard and risk analyses during planning - Challenge: Complex verification processes
Solution: Adopt Model-Based Verification and qualified tools compliant with DO-330
Requirements Gathering for DO-254 Compliance
Importance of Requirements Definition and Traceability
Accurate and detailed requirements are essential for successful hardware development and certification under DO-254. Traceability ensures that every requirement is linked to design, verification, and certification artifacts, facilitating comprehensive compliance proof.
Best Practices for Gathering and Specifying Avionics Hardware Requirements
- Early and Collaborative Requirements Definition: Involve cross-functional teams during the requirements elicitation process.
- Specification of Testable Requirements: Define requirements in measurable terms for easier verification.
- Traceability Automation: Use traceability tools to manage links between requirements, design, and testing.
- Iterative Requirement Reviews: Conduct regular reviews to refine and validate requirements.
By following these structured approaches, avionics hardware teams can streamline DO-254 compliance and maintain high levels of safety and quality assurance.
DO-254 Verification and Validation (V&V) Process
Importance of Aviation Verification and Validation
Verification and validation (V&V) are critical components of the DO-254 process, ensuring that airborne electronic hardware meets design requirements and functions reliably under all operating conditions. Proper V&V mitigates hardware failures, enhances safety, and supports certification by providing essential compliance evidence.
Key Benefits of Effective V&V in DO-254:
- Early Error Detection: Identifies design flaws early, reducing costly rework.
- Compliance Proof: Demonstrates compliance with regulatory requirements, supporting airworthiness certification.
- Improved Safety: Ensures hardware reliability in safety-critical avionics systems.
Steps Involved in the DO-254 V&V Process
- Verification Planning:
- Develop a Hardware Verification and Validation Plan (HVVP)
- Define verification methods, tools, and test strategies
- Identify test environments and configuration requirements
- Requirement Analysis:
- Ensure requirements are complete, consistent, and testable
- Establish traceability between requirements and test cases
- Verification Activities:
- Perform simulation, analysis, and hardware testing
- Conduct design reviews and inspections
- Validation Activities:
- Validate that the hardware performs intended functions under operational conditions
- Confirm compliance with safety and certification requirements
- Traceability and Reporting:
- Maintain traceability between requirements, design, and test artifacts
- Document verification results and generate certification evidence
Model-Based Development and Verification (RTCA DO-331)
RTCA DO-331 provides guidance on using Model-Based Development (MBD) and Model-Based Verification (MBV) for airborne systems. It complements DO-254 by allowing teams to leverage models for the design and verification of complex hardware components.
Benefits of Model-Based Development and Verification:
- Accelerated Development: Speeds up design iterations using simulation models.
- Enhanced Accuracy: Detects design issues earlier through model-based simulations.
- Improved Traceability: Maintains consistent traceability between models and requirements.
Best Practices for DO-254 Compliance with Model-Based Verification:
- Use qualified tools compliant with RTCA DO-330 for modeling and verification.
- Maintain comprehensive traceability between requirements, models, and test results.
- Validate models against actual hardware implementations to ensure accuracy.
By integrating MBD and MBV approaches with traditional verification techniques, organizations can significantly streamline their DO-254 V&V processes, reduce development timelines, and improve hardware design accuracy.
Traceability and Testability in DO-254
Requirements Traceability for DO-254
Traceability is a cornerstone of DO-254 compliance, ensuring that every requirement is consistently linked to design, verification, and certification activities. This linkage enables comprehensive proof of compliance and supports effective certification audits.
Key Benefits of Traceability in DO-254
- Compliance Evidence: Provides clear links between requirements and their implementation, supporting certification audits.
- Change Impact Analysis: Identifies affected components when requirements change, reducing errors and rework.
- Verification Validation: Ensures all requirements are tested and validated during the V&V process.
Testability Best Practices for Avionics Hardware
Testability refers to the ease with which hardware can be tested to verify its compliance with specified requirements. Ensuring high testability is critical for achieving successful DO-254 certification.
Best Practices for Hardware Testability
- Requirement Definition: Write clear, measurable, and testable requirements.
- Early Testing: Perform testing at the design phase to identify defects early.
- Simulation and Analysis: Use simulation tools to test complex electronic hardware (CEH), including FPGAs and ASICs.
- Design for Testability (DfT): Incorporate test points and access features into hardware designs to facilitate testing.
- Continuous Testing: Conduct iterative and automated testing throughout the development lifecycle.
Automated Traceability Solutions for DO-254
Automation plays a vital role in managing the complex traceability requirements of DO-254. Automated traceability tools significantly reduce manual effort, enhance accuracy, and improve compliance outcomes.
Benefits of Automated Traceability
- Real-Time Traceability: Immediate updates to traceability matrices as requirements, design, and tests evolve.
- Error Reduction: Minimizes human errors associated with manual tracking.
- Audit Readiness: Generates traceability reports and evidence for certification authorities.
Key Features of Automated Traceability Tools
- Bidirectional Requirement Traceability: Links between requirements, tests, and design artifacts.
- Change Impact Analysis: Identifies how changes in requirements affect related components.
- Compliance Reporting: Automated generation of documentation required for certification.
By adopting automated traceability solutions, organizations can streamline DO-254 compliance, improve hardware testability, and ensure seamless certification processes for airborne electronic hardware development.
RTCA DO-330 and Tool Qualification
Significance of DO-330 for Tool Qualification
RTCA DO-330, titled Software Tool Qualification Considerations, provides guidance on the qualification of tools used in safety-critical systems, including DO-254 for airborne electronic hardware. The standard ensures that tools used in development, verification, and certification do not introduce errors or compromise safety.
Why DO-330 Qualification Matters?
- Safety Assurance: Ensures the accuracy and reliability of tools used in hardware development.
- Certification Support: Demonstrates compliance with certification requirements by validating tool performance.
- Error Prevention: Reduces risks associated with using unqualified tools in safety-critical processes.
Levels of Tool Qualification
DO-330 defines qualification levels based on the tool’s role and its potential impact on the end product:
- TQL-1: Highest qualification level for tools that can directly introduce errors.
- TQL-5: Lowest level for tools with minimal impact on development.
Automation in DO-254 Using Qualified Tools
Automation is essential for handling the complexities of DO-254 compliance and certification. Using DO-330-qualified tools allows for efficient development, verification, and documentation processes.
Benefits of Automation:
- Efficiency: Speeds up design, testing, and compliance reporting.
- Error Reduction: Minimizes manual errors in traceability and testing.
- Audit Readiness: Generates automated compliance reports for certification authorities.
Key Use Cases for Automation in DO-254:
- Automated Traceability: Real-time updates between requirements and test cases.
- Verification Automation: Automated execution of test cases for validation.
- Documentation Generation: Automated creation of evidence for certification audits.
By leveraging DO-330-qualified tools, organizations can ensure compliance with DO-254, reduce manual workload, and improve the overall efficiency of avionics hardware development. Visure Requirements ALM stands out as a leading solution for automated traceability and compliance management, supporting DO-330 qualifications.
Commercial Off-the-Shelf (COTS) Components and DO-254
Commercial Off-the-Shelf (COTS) components are pre-developed hardware parts, often used in avionics to reduce costs and development time. Examples include microcontrollers, processors, FPGAs, and other integrated circuits. Despite their benefits, COTS components must adhere to strict guidelines to meet DO-254 compliance for airborne electronic hardware.
Role of COTS in Avionics Hardware
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces the need for custom development.
- Time Savings: Accelerates development timelines by leveraging readily available solutions.
- Standardization: Provides industry-proven, tested components.
Challenges of Using COTS in Avionics Hardware
- Limited Access to Design Data: Manufacturers may not share detailed design or testing information.
- Verification and Validation Complexity: Difficulty in verifying COTS components against DO-254 requirements.
- Obsolescence Risks: COTS components may become obsolete without warning.
- Traceability Issues: Ensuring full traceability for certification when using COTS components can be difficult.
What is Proof of Compliance for DO-254?
Proof of compliance for DO-254 refers to the documented evidence that an avionics hardware development project meets the safety and reliability requirements outlined by the standard. This evidence is critical for achieving certification from aviation authorities like the FAA and EASA.
Key Elements of Proof of Compliance:
- Requirement Traceability: Demonstration of traceability from requirements to design, verification, and validation.
- Verification Reports: Test results proving that hardware functions as intended without safety risks.
- Design and Process Artifacts: Documentation including the Hardware Design Plan (HDP), Hardware Verification Validation Plan (HVVP), and Plan for Hardware Aspects of Certification (PHAC).
- Safety of the Intended Function (SOI) Audits: Certification bodies assess compliance during SOI audits at different project milestones.
Automated Proof of Compliance for DO-254
Automation in compliance verification can greatly simplify and accelerate the process of generating and managing evidence required for DO-254 certification. Automated tools streamline the development lifecycle by linking requirements, design elements, and test results while maintaining traceability.
Some of the Top Automated Tools:
- Requirements Management Tools: Automate requirement definition and traceability (e.g., Visure Requirements ALM).
- Verification Automation Tools: Automate test execution and validation processes.
- Traceability Solutions: Ensure bidirectional traceability between requirements and validation data.
- Documentation Generators: Automate the creation of compliance reports for audits.
Benefits of Automation in Compliance Verification
- Enhanced Accuracy: Reduces manual errors in documentation and traceability.
- Time Efficiency: Speeds up verification and validation processes, reducing development timelines.
- Cost Savings: Minimizes resources required for compliance activities.
- Real-Time Traceability: Provides dynamic, up-to-date traceability between requirements and test cases.
- Audit Readiness: Ensures the availability of comprehensive and well-structured compliance evidence for certification authorities.
- Scalability: Easily adapts to project complexities and changes.
By leveraging automated solutions, companies can achieve faster and more reliable proof of compliance for DO-254, improve traceability management, and enhance audit readiness, ensuring efficient avionics hardware certification.
Visure Solutions for DO-254 Compliance
Visure Solutions offers a comprehensive platform tailored to support DO-254 compliance for avionics hardware development. By providing advanced requirements management and traceability tools, Visure ensures organizations can meet the stringent demands of RTCA DO-254 while improving efficiency and reducing risks.
How Visure Solutions Supports DO-254 Compliance?
- Robust ALM and Requirements Management
- Centralized repository for managing requirements, hardware specifications, and verification artifacts.
- Enables teams to manage Functional Design Assurance Level (FDAL) and Item Design Assurance Level (IDAL) effectively.
- Streamlines requirements gathering and refinement processes for DO-254 projects.
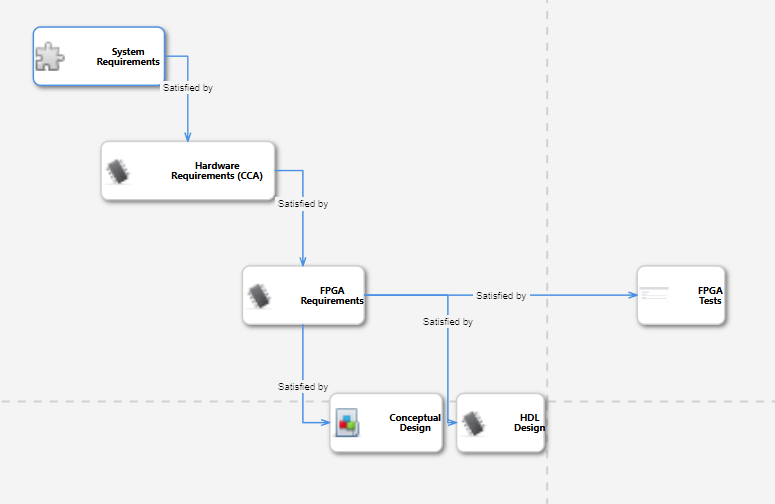
- Bi-Directional Traceability
- Ensures end-to-end traceability between requirements, hardware design, test cases, and verification results.
- Automates traceability reporting for Safety of the Intended Function (SOI) audits.
- Facilitates compliance with standards like RTCA DO-254, DO-331, and DO-330.
- AI-Assisted Requirements Generation
- Requirements generation for avionics hardware projects.
- Automatic risk generation for critical systems.
- Test case and user story generation tailored to DO-254 processes.
- Specification template generation for PHAC, HDP, and HVVP.
- Requirements quality analysis to ensure standards compliance.
- Mapping applicable standards like RTCA DO-254, DO-331, and DO-330.

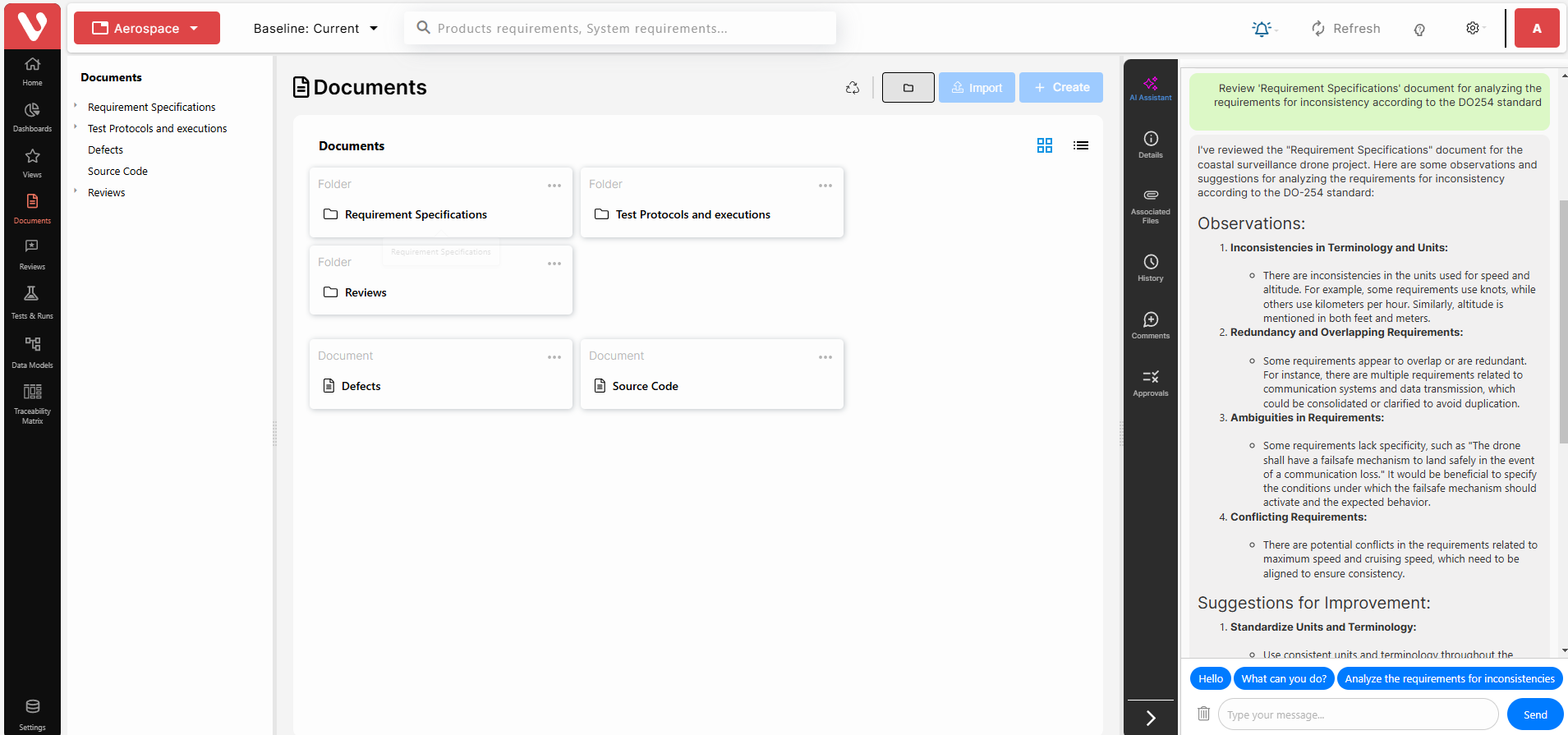
- Vivia (Visure Virtual Assistant)
- AI-powered assistant that simplifies DO-254 compliance processes.
- Helps in identifying gaps, generating compliance artifacts, and automating documentation.
- Provides intelligent insights for improving requirements quality and project efficiency.
- Verification & Validation
- Supports the DO-254 verification and validation (V&V) process by linking requirements with test results.
- Integrates with model-based verification tools compliant with RTCA DO-331.
- Provides automated compliance evidence for certification readiness.
- Advanced Risk and Change Management
- FMEA plugin for comprehensive risk analysis.
- Baseline management for tracking changes across development milestones.
- Impact analysis to evaluate how changes affect project compliance and deliverables.
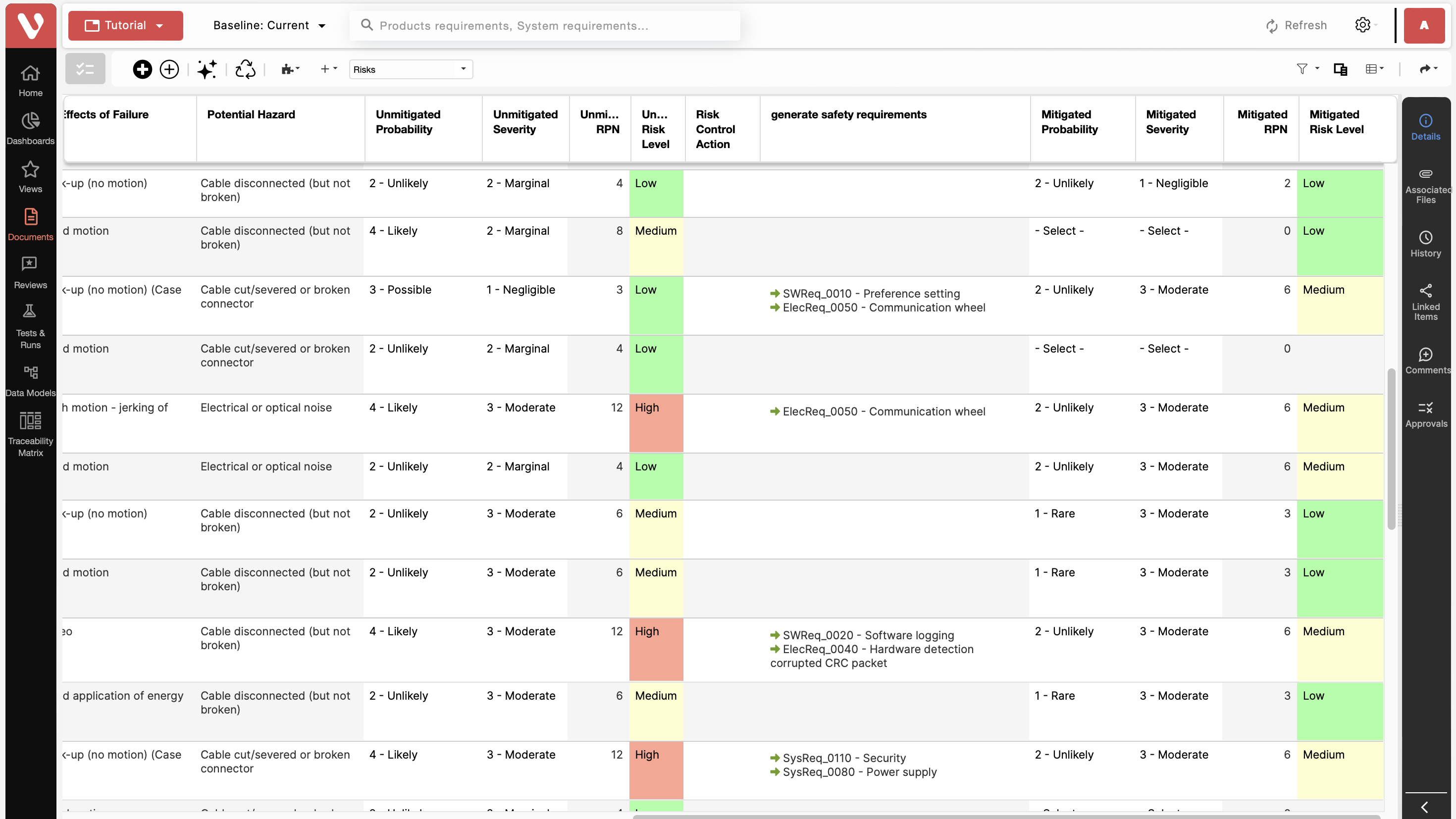
- Seamless Integration
- Import-export capabilities with MS Word and Excel, facilitating easier document management.
- Integration with industry-standard tools such as ConsuNova, Rapita Systems, and IBM DOORS for enhanced workflows.
Benefits of Using Visure for Avionics Hardware Development
- Streamlined DO-254 Compliance: Automation of requirements management, traceability, and proof of compliance reduces manual effort and improves audit readiness.
- Improved Accuracy and Quality: AI-powered tools ensure high-quality requirements and reduced errors in compliance artifacts.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Centralized management and bi-directional traceability speed up project timelines.
- Simplified Certification: Automated generation of PHAC, HDP, HVVP, and other compliance documentation ensures audit readiness.
- Real-Time Collaboration: Enables effective communication between stakeholders, improving project outcomes.
- Scalable Solution: Adapts to the complexity of avionics hardware projects, including CEH such as FPGAs and ASICs.
By leveraging Visure Solutions, avionics organizations can navigate the challenges of DO-254 compliance, improve traceability, and achieve faster, cost-effective hardware certification.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of DO-254 compliance for airborne electronic hardware, including CEH like FPGAs and ASICs, requires a well-structured approach to requirements management, verification, and validation. By embracing best practices, automation, and qualified tools, organizations can ensure compliance while reducing development timelines and certification risks.
Visure Solutions stands out as a powerful partner in this journey, offering a robust platform for end-to-end requirements management, traceability, AI-assisted compliance processes, and automated proof of compliance. With features like Vivia (Visure Virtual Assistant) and bi-directional traceability, Visure empowers engineering teams to simplify audits, enhance project efficiency, and achieve seamless DO-254 certification.
Start your 14-day free trial at Visure today and experience streamlined compliance like never before.
