Organizations are constantly seeking new ways on how to improve performance and streamline processes. The Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) model has helped many organizations achieved demonstrable business results, and implementing it in practice has never been easier thanks to modern CMMI tools.
Who create CMMI?
Developed at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) and required by many United States Department of Defense (DoD) and U.S. Government contracts, the purpose of CMMI is to provide a clear roadmap of best practices that organizations should follow to elevate and benchmark performance across a range of critical business capabilities.
CMMI is the successor of the capability maturity model (CMM), or Software CMM for short. As its name suggests, Software CMM was tailored to software engineering. The latest version of CMMI (Version 2.0) was released in 2018, and it allows the model to be applied to hardware, software, and service development across every industry.
What is CMMI?
CMMI (Capability Maturity Model Integration) describes the best practices, already applied in the industry, to develop, maintain and acquire products and services. It provides a framework that allows to assess the level of maturity in an organization or its capability in relation with the processes it performs, to set priorities in order to put into practice the improvements that have to be carried out and to realize those improvements.
There are 3 CMMI models, all of them developed by the Software Engineering Institute (SEI), a Research & Development centre that is part of the Carnegie Mellon University, in Philadelphia; these models are:
- CMMI for Development, addressed to organizations that develop and maintain products and services for system development.
- CMMI for Acquisition, addressed to organizations that subcontract development services and maintain products and services for system development.
- CMMI for Services, addressed to organizations that provide services to other companies.
The aims of CMMI are:
- To provide a framework which helps the organization to improve its processes
- To provide a guide to improve the capacity to develop, to acquire and maintain products or services provided by an organization.
- To describe a set of best practices, both in management and engineering.
In the last few years, CMMI has acquired enormous importance as a quality system in the systems industry, and can practically be considered the de facto standard in this area. Nevertheless, CMMI can be applied to different areas, such as systems engineering, hardware, etc. CMMI for Development is applied to the development and maintainance of products and services, regardless of the field or area of interest. The current version of CMMI is the document “CMMI for Development”,version 1.2, available since August 2006.
The main elements in the CMMI for Development model are Process Areas; within each Process Area, CMMI identifies a set of Specific and Generic Objectives, as well as a set of Practices that should be implemented in order to achieve these Objectives and cover each of the Process Areas.
What are the 5 levels of CMMI?
CMMI Model considers 5 maturity levels, measurable for the organization:
- Initial
- Managed
- Defined
- Quantitatively managed
- Optimizing
In maturity level 1 (Initial), the organization is characterised by the ad-hoc nature of its processes. The organization does not provide a stable environment for the creation of its products, so the success of its projects depends exclusively on the skills of the individuals dedicated to each of them.
In maturity level 2 (Managed), projects in the organization perform processes according to what is planned and defined in the organization policies, employing skilled people who possess the required knowledge, involving all relevant stakeholders, and monitoring, controlling and reviewing all processes.
In maturity level 3 (Defined), all processes are understood and described through standards, procedures, tools and methods.
In maturity level 4 (Quantitatively Managed), the organization and projects establish quantitative objectives to measure process quality as well as its use, and needed criteria to manage them. Statistical methods are used to control processes.
In maturity level 5 (Optimizing), the organization applies continuous improvement of its processes through quantitative understanding of the causes of variation common to the process, using statistical methods that endorse continuous improvement.
Maturity levels are cumulative, in other words, to reach each of them it is necessary to implement all specific process areas in that level as well as all lower levels.
What are the 6 capability levels of CMMI?
In turn, CMMI Model considers 6 capability levels, measurable for each process:
- Incomplete
- Performed
- Managed
- Defined
- Quantitatively Managed
- Optimizing
CMMI Capability Level 0 (Incomplete): partially performed. One or more Specific Objectives of the Process Area are not fulfilled.
CMMI Capability Level 1 (Performed): It is an Incomplete process that satisfies all Specific Objectives in the Process Area.
CMMI Capability Level 3 (Managed): It is a Performed process, that possesses the needed infrastructure to support process, so that the process is performed according to what is planned and defined in the organization policies, employing skilled people who possess the required knowledge, involving all relevant stakeholders, and monitoring, controlling and reviewing the process.
CMMI Capability Level 3 (Defined): It is a Managed process that is tailored from the organization set of standard processes according to its tailor guides, and that contributes products, measures, etc. to the organization improvement.
CMMI Capability Level 4 (Quantitatively Managed): It is a Defined process that is controlled using statistical techniques.
CMMI Capability Level 5 (Optimizing): It is a Quantitatively Managed process that is improved through quantitative understanding of the causes of variation common to the process.
Capability levels are cumulative.
What are CMMI’s Representations?
The Model states two representations:
- Staged representation
- Continuous representation
In both cases, Process Areas, Objectives and Practices are the same. The difference between these representations is the order in which process improvement is implemented:
- In the case of staged representation, process areas to be improved are chosen in a predefined sorting given by its assignment to maturity levels of the Model.
- In the case of continuous representation, processes to be improved are selected in the sorting the organization deems most appropriate based on its business aims. For each Process Area there are capability levels (from 0 to 5) that provide an indication of the sorting in which the improvement should be dealt with within each of them.Continuous representation is closer to other quality standards such as ISO 15504 (SPICE). Staged representation corresponds to the first versions of the CMMI model, formerly CMM, and which only contemplated implementation based on theorganization’s maturity levels.
How Can CMMI Help Your Organization?
CMMI can help organizations in a number of important ways:
- Increases customer satisfaction.
- Improves the chance of landing and retaining new clients.
- Increases productivity and efficiency.
- Creates more profits.
- Increases the ability to meet project goals and business objectives.
- Makes it easier to deal with risk and uncertainty.
- Helps identify skill gaps and break down workflow bottlenecks.
- Promotes communication with organization-wide standards.
The latest version of CMMI is written in non-technical language, which makes it more user-friendly and easier to implement. Organizations can explore CMMI online and configure it based on their specific goals for performance improvement and organizational success. Tools like Visure Requirements help improve maturity by monitoring and tracing requirements and helping standardize and harmonize the application of business processes.
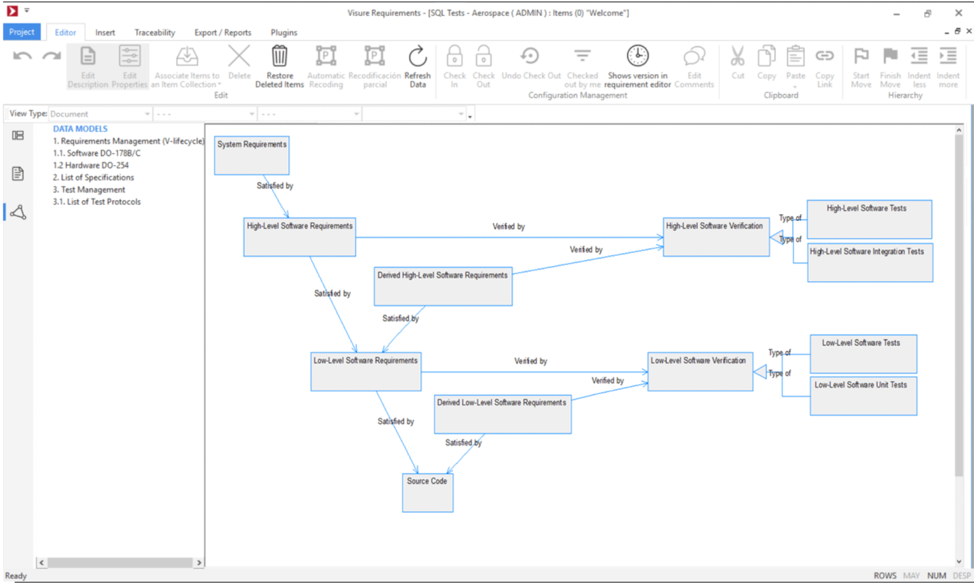
Using a Requirement Management tool to support CMMI
Visure Requirements shares with CMMI this approach: requirements management is closely linked with requirements development. A Requirements Engineering process supported by Visure Requirements includes not only activities specific to requirements management, such as the unambiguous identification of requirements, versioning, traceability, etc. but also others such as definition of business models and interfaces, and the identification of functionalities of the system to be developed. The management of these activities within the same tool is a significant advantage as it helps participants in the project to maintain an overall, integrated vision of all activities as part of a cyclic and iterative process.
Additionally, the use of Visure Requirements as a support for the implementation of CMMI has many benefits as it allows to automate part of the processes, ensuring fulfillment of processes even in moments of stress, such as it is required in the description of CMMI level 2 (Managed).

In fact, already in CMMI for Development level 2, among the resources considered as necessary to support the activities, as one of the “typical work products”, it is recommended to use a tool to monitor and trace requirements. The reason for this is that manual maintenance is so costly that the risk of abandoning best practice is very high if such a tool is not available.
For maturity level 3 (Defined), the organization must have general processes defined, which will be tailored to the different projects as needed. Also, these processes must be properly characterized, understood and described in standards, processes, tools and methods, providing templates to support process standardisation. Here, the use of Visure Requirements facilitates the implementation of requirements processes at level 3, as it helps to standardise and harmonise the application of processes along the company.
For maturity levels 4 (Quantitatively Managed) and 5 (Optimizing), it is necessary to identify the sub processes that make the most significant contribution to the general process, to be checked and managed using a set of statistical and quantitative techniques, which make it possible to improve the definition and implementation of processes in the organization. It is also of interest here the use of a tool, as quantitative management is not possible without the storage of data that can subsequently be exploited for the calculation of metrics and the development of performance models or process behavioural models.
Continue reading the full White-paper





